Direct Thermal vs. Thermal Transfer Printing: When to Choose Which
Posted by Thermal Printer Supplies on Feb 22nd 2025
Have you ever wondered how the label on that package you received was printed? Or how the cashier prints your receipt so quickly? Chances are, it was done using thermal printing technology. Thermal printing uses heat to create an image on a label or other media. There are two main types of thermal printing: direct thermal and thermal transfer. Both methods utilize a thermal printhead that applies heat to the printing surface, but they differ in how the image is created. This article will explore the differences between direct thermal and thermal transfer printing, their common applications, and when it's best to use each method, with a particular focus on when direct thermal printing is no longer a viable option and thermal transfer becomes the preferred choice. A key factor in making this decision is the required lifespan of the label.
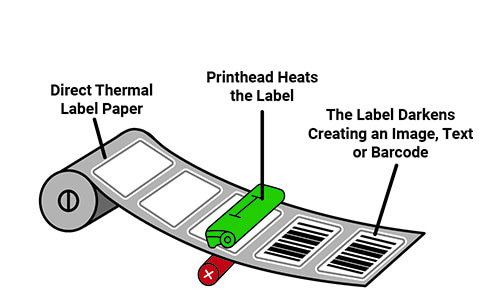
Direct Thermal Printing
Direct thermal printing uses chemically treated, heat-sensitive media that blackens when it passes under the thermal printhead. This means that no ink, toner, or ribbon is required. The label material itself is coated with a heat-sensitive layer that changes color when heated. This makes direct thermal printers simple to operate and maintain, as there are no messy consumables to replace.
|
Advantages of Direct Thermal Printing Cost-Effective: Direct thermal printing eliminates the need for ink, toner, or ribbons, resulting in lower operational costs. Simplicity & Ease of Use: Direct thermal printers are relatively simple to operate, with fewer components and maintenance requirements. Compact & Mobile: Due to their simpler, ribbon-free mechanics, direct thermal printers are more compact, and most mobile printers use direct thermal technology. Fast Printing Speeds: Direct thermal printing is known for its fast printing speeds, making it suitable for high-volume printing environments where time is critical. For example, a direct thermal printer like the Munbyn 941U can print at a speed of 6 inches per second. Short-Term Labeling: Direct thermal labels typically have a lifespan of 6-8 months, making them suitable for applications where the label doesn't need to last for an extended period. |
Disadvantages of Direct Thermal Printing Sensitivity to Heat & Sunlight: Direct thermal prints are susceptible to fading or darkening when exposed to extreme temperatures or other sources of intense light. Limited Durability: Direct thermal prints are less durable compared to prints produced through thermal transfer. The printed image can be easily scratched, smudged, or damaged by moisture or chemicals. Limited Color Options: Direct thermal printing is primarily used for monochrome or black-and-white printing. While some direct thermal printers offer limited color options, they are generally not capable of producing full-color prints. Shorter Printhead Lifespan: The print head in direct thermal printers may experience more wear and tear due to direct contact with the chemically treated thermal paper, leading to a shorter lifespan. This is further exacerbated by the fact that dust and debris on labels can come into direct contact with the printhead and cause damage. In contrast, the ribbon in thermal transfer printing acts as a buffer, protecting the printhead from such damage. |
Common Applications of Direct Thermal Printing
Direct thermal printing is best suited for applications where the label does not need to last very long or be exposed to harsh conditions. Common applications include:
|
Shipping Labels: Direct thermal labels are commonly used for shipping labels because they are cost-effective and can be printed quickly. Receipts: Direct thermal printing is widely used for receipts due to its speed and low cost. Tickets: Direct thermal printers are used to print tickets for events, transportation, and other applications where a temporary label is sufficient. |
Labels for Perishable Goods: Direct thermal labels are suitable for labeling perishable goods that have a short shelf life. Name Tags: Direct thermal printers can be used to create name tags for events or conferences. |
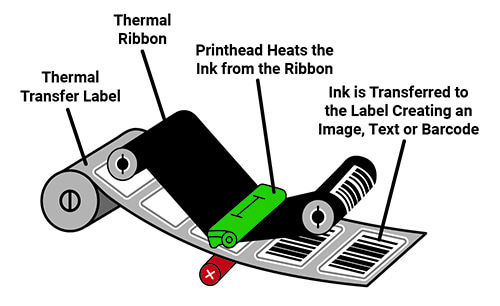
Thermal Transfer Printing
Thermal transfer printing uses a heated ribbon to produce durable, long-lasting images on a wide variety of materials. The ribbon contains a wax or resin-based ink that is melted onto the printing media by the thermal printhead. This creates a more durable and long-lasting image compared to direct thermal printing.
| Advantages of Thermal Transfer Printing | Disadvantages of Thermal Transfer Printing |
|---|---|
|
Print Quality: Thermal transfer printing produces high-quality prints with excellent resolution, sharpness, and clarity. Print Durability: Prints are highly durable and resistant to heat, moisture, chemicals, and UV exposure. Extended Print Head Life: The print head lasts longer since it doesn’t contact chemically treated label material directly. |
Higher Cost: Thermal transfer printing is more expensive due to the additional cost of ribbons. Complexity & Maintenance: These printers require regular maintenance, including print head cleaning and ribbon replacement. Environmental Considerations: Ribbon usage generates waste, though a longer printhead lifespan may offset this. |
|
Flexibility in print options: Works with various ribbon types and colors, supporting paper, plastic, and polyester labels. Long-term labeling: Labels can last up to 2 years, ideal for applications requiring longevity. |
Slower Print Speed: Typically prints slower than direct thermal printers. For example, the Zebra GK420t prints at 5 inches per second. |
Common Applications of Thermal Transfer Printing
Thermal transfer printing is ideal for applications where durability and longevity are essential. Common applications include:
|
Product Identification: Thermal transfer labels are used for product identification, providing long-lasting and durable labels that can withstand harsh environments. This is particularly important in industries like logistics, where barcodes are used to track products throughout the supply chain. Inventory Tracking: Thermal transfer printing is used for inventory tracking labels, ensuring that labels remain readable and scannable over time. Packaging Information: Thermal transfer labels are used on packaging to provide important information about the product, such as ingredients, instructions, and warnings. This is especially important for products that require long-term labeling, such as appliances, where the label needs to display the date of manufacture, serial numbers, and other essential details. |
Laboratory Specimens & Blood Bags: Thermal transfer labels are used in healthcare settings to label specimens and blood bags, ensuring that critical information remains intact. Outdoor Applications: Thermal transfer labels are suitable for outdoor applications, as they can withstand exposure to sunlight, rain, and other weather conditions. This makes them ideal for labeling products like fresh produce, which may be stored outdoors or exposed to varying temperatures. Asset Tracking: Thermal transfer labels are used for asset tracking, providing durable labels that can be attached to equipment and other valuable assets. Thermal transfer labels are one of the best options for asset tagging due to their durability and longevity. |
| Feature | Direct Thermal | Thermal Transfer |
|---|---|---|
| Print Method | Direct Thermal Printing uses chemically treated, heat-sensitive media that blackens when it passes under the thermal printhead. | Thermal Transfer printing uses a heated ribbon to produce durable, long-lasting images on a wide variety of matierals. |
| Durability | Lower cost. | Higher cost. |
| Lifespan | 6 to 8 months. | Up to 2 years. |
| Cost | Lower intitial cost, but may be less cost-effective for high-volume printing. | Higher intitial cost, but can be more cost-effective in the long run. |
| Speed | Faster speed. | Lower speed. |
| Color Options | Limited color options. | A wide range of colors available. |
| Ideal Use Cases | Shipping labels, receipts, tickets, & labels for perishable goods. | Product identification, inventory tracking, packaging information, laboratory specimens, outdoor applications, & asset tracking. |
|
Cost Considerations |
Types of Thermal Labels |
Environmental Impact |
When Direct Thermal is No Longer an Option
While direct thermal printing offers cost-effectiveness and simplicity, there are certain situations where it is no longer a viable option. These include:
|
Long-Term Labeling Harsh Environments High-Durability Requirements |
Need for Color Printing Regulatory Requirements |
In Conclusion: How to Choose the Best Printing Technology
Direct thermal and thermal transfer printing are both valuable technologies with their own strengths and weaknesses. Direct thermal printing is a cost-effective and simple solution for short-term labeling needs, while thermal transfer printing offers durability and longevity for applications where labels need to withstand harsh environments or last for an extended period. The required lifespan of the label is a crucial factor in determining the appropriate printing method. By understanding the differences between these two methods, businesses can choose the best printing technology for their specific needs.
Talk to an Expert
